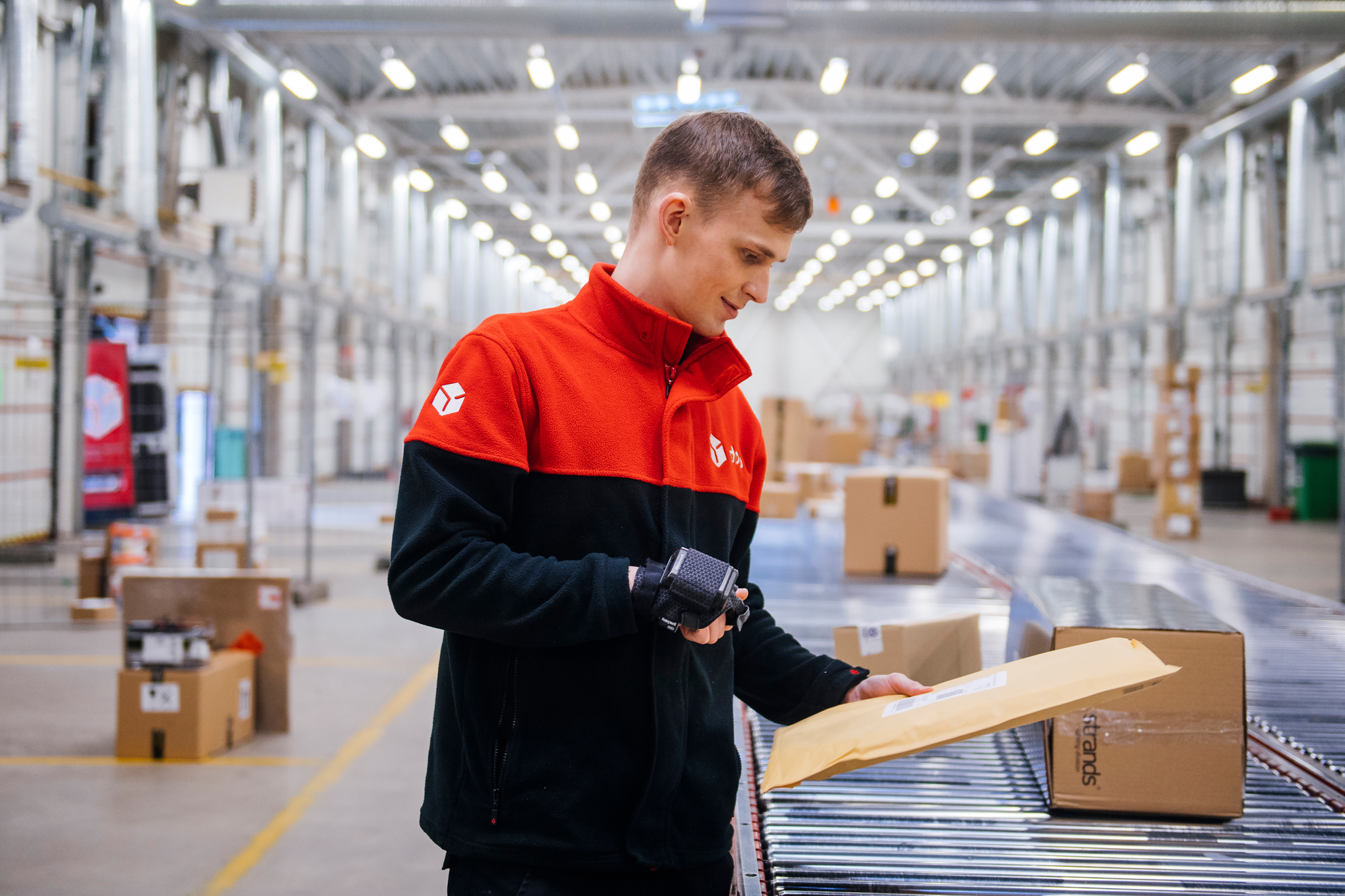
Customs formalities
Customs formalities for the goods need to be completed when sending goods from Estonia to Norway, Switzerland, United Kingdom and Åland. According to the legislation, customs formalities must be completed regardless of whether the sender is a company or a private individual and whether the recipient is a company or a private individual.
Check out the formalities
Customs formalities when shipping to the UK
-
In addition to the correct parcel label the sender should attached next document to the parcel: Export declaration in one copy, Invoice (or proforma-invoice) in at least three copies. Documentation should be in English, put into the plastic pocket and attached to the package.
-
The information about the sender and recipient (company name, address) must be the same on the shipment's customs documents (invoice, delivery note, etc.) and on the parcel label.
-
The goods are automatically returned if customs documents are missing or if the shipment is oversized. The goods are stored at the customs checkpoint for up to 7 business days if the Sender/Recipient data is inaccurate or needs to be added.
-
More information on arranging customs procedures relevant upon sending parcels to the United Kingdom can be viewed here.
Customs formalities when shipping to Norway, Switzerland and Åland
-
Upon sending a parcel out of the European Union, in the absence of customs documents, a claim of 25 euros will be added to the price.
DPD is not responsible for the preparation of customs documents and the accuracy and sufficiency of the information contained therein, as well as for the payment of customs duties and VAT. If a DPD representative has paid customs and/or VAT on behalf of the recipient and the recipient fails to perform its obligations to the DPD representative, DPD has the right to demand the payment of the amount unpaid by the recipient from the customer. -
If the value and / or weight of the goods exceeds €1,000 / 1,000 kg, the sender of the goods shall declare the goods to the Estonian customs agency. The sender of the goods shall attach 1 copy of the declaration to the invoice in a plastic bag.
-
The goods must be accompanied by an invoice (5 copies). The invoice must be in a document pocket affixed to the packaging.
-
If the goods have all the necessary and required customs documents, then usually customs formalities are arranged for the goods within 1 working day after the arrival of the goods in the country of destination. The goods are then available for delivery.
-
The goods are automatically returned if customs documents are missing or if the shipment is oversized. The goods are stored at the customs checkpoint for up to 7 business days if the Sender/Recipient data is inaccurate or needs to be added.
-
All major customs brokerage companies can provide more detailed information about the requirements for arranging export customs formalities. For example, A-Tolliagentuur. A brokerage company of the country of destination can provide the most accurate answers to the sender’s questions regarding the terms and conditions and legislation of import customs formalities.
Check out the formalities


Customs formalities when shipping to the UK
-
In addition to the correct parcel label the sender should attached next document to the parcel: Export declaration in one copy, Invoice (or proforma-invoice) in at least three copies. Documentation should be in English, put into the plastic pocket and attached to the package.
-
The information about the sender and recipient (company name, address) must be the same on the shipment's customs documents (invoice, delivery note, etc.) and on the parcel label.
-
The goods are automatically returned if customs documents are missing or if the shipment is oversized. The goods are stored at the customs checkpoint for up to 7 business days if the Sender/Recipient data is inaccurate or needs to be added.
-
More information on arranging customs procedures relevant upon sending parcels to the United Kingdom can be viewed here.
Customs formalities when shipping to Norway, Switzerland and Åland
-
Upon sending a parcel out of the European Union, in the absence of customs documents, a claim of 25 euros will be added to the price.
DPD is not responsible for the preparation of customs documents and the accuracy and sufficiency of the information contained therein, as well as for the payment of customs duties and VAT. If a DPD representative has paid customs and/or VAT on behalf of the recipient and the recipient fails to perform its obligations to the DPD representative, DPD has the right to demand the payment of the amount unpaid by the recipient from the customer. -
If the value and / or weight of the goods exceeds €1,000 / 1,000 kg, the sender of the goods shall declare the goods to the Estonian customs agency. The sender of the goods shall attach 1 copy of the declaration to the invoice in a plastic bag.
-
The goods must be accompanied by an invoice (5 copies). The invoice must be in a document pocket affixed to the packaging.
-
If the goods have all the necessary and required customs documents, then usually customs formalities are arranged for the goods within 1 working day after the arrival of the goods in the country of destination. The goods are then available for delivery.
-
The goods are automatically returned if customs documents are missing or if the shipment is oversized. The goods are stored at the customs checkpoint for up to 7 business days if the Sender/Recipient data is inaccurate or needs to be added.
-
All major customs brokerage companies can provide more detailed information about the requirements for arranging export customs formalities. For example, A-Tolliagentuur. A brokerage company of the country of destination can provide the most accurate answers to the sender’s questions regarding the terms and conditions and legislation of import customs formalities.
-
TOLL
Customs duty and VAT
If customs formalities are arranged by DPD Norway / Switzerland or its representative, the invoice for customs duties shall generally be issued to the sender within 1 week after the arrangement of the customs formalities. The goods shall be delivered to the recipient immediately after the completion of customs formalities. The recipient usually has 30 calendar days to pay the customs duties. If the fee has not been paid on time, the first reminder will be sent and the recipient will usually be given an additional 15 calendar days. If the fee has not been paid by this point, a second reminder will be sent and if the fee is not paid, the corresponding invoice will be forwarded to DPD Estonia. DPD Estonia in turn will forward it to the sender.
We therefore recommend that you make sure you have an explicit agreement with the recipient regarding who covers the costs related to the completion of customs formalities and, as much as possible, verify the recipient\'s solvency and proceed based on the information received.
For more information on taxes within Norway: http://www.toll.no/en/corporate/import/and http://www.toll.no/en/online-shopping/.
Invoice
Mandatory when sending goods to Norway or Switzerland. Goods must be accompanied by 5 copies of the invoice, of which 1 copy also reaches the final recipient. The invoice must indicate the correct value of the product, even in the case of presents and documents. The value of the goods must never be 0. If documents have no value, even the price of the paper must be indicated. The invoice language should be English.
Required fields of an invoice are:
-
Name and address of sender, registry number
-
The EORI code – obligatory for all companies engaged in foreign trade in exporting, importing, transit and other customs operations. It is even mandatory for a one-off shipment outside the European Union. In Estonia, the EORI code is issued by the Estonian Tax and Customs Board. The company’s legal representative may request the number.
-
Name and address of the consignee
-
Invoice number and date
-
Seller’s reference
-
Buyer’s reference
-
Buyer\'s name (if it differs from the consignee\'s)
-
Delivery address
-
Delivery terms – indicates the amount of shipping costs included in the submitted invoice. The delivery terms, together with the name of the populated area, indicate the extent to which it applies.
-
Country of destination
-
Country of dispatch
-
Place of unloading
-
Final destination
-
Customs code of goods i.e. the taric code – a 10-digit articulated code provided by the declarant.
-
Name of the goods (as precise as possible) – if the name is incorrect, the goods may be returned by the customs.
-
Gross weight, net weight
-
Quantity, number of parcels
-
Price per unit
-
Currency
-
Signature and stamp of the exporter
If the goods are insured, this must also be indicated on the invoice.
EORI number
The EORI number is obligatory for companies engaged in foreign trade in exporting, importing, transit and other customs operations.
The Economic Operators Registration and Identification (EORI) system was set up to implement security measures. Security measures are more effective if the persons concerned can be identified by a single number which is unique for each individual and valid throughout the community.
In Estonia, the EORI code is issued by the Estonian Tax and Customs Board.
Additional information: http://www.emta.ee/et/ariklient/toll-kaubavahetus/ettevotja-registreerimine-eori
Welcome to the DPD website / Customs formalities